Discover the Secrets of Growing Premium Cannabis at Home
Are you tired of overpaying for subpar cannabis at dispensaries? What if I told you that you could grow your own top-shelf buds right from the comfort of your own home, 100% legally? My name is Adam, and I've been successfully cultivating cannabis for over a decade. Through trial and error, I've developed foolproof methods for growing potent, flavorful buds that rival anything you'd find in a dispensary.
Who Is Cannabis Khan?
Discover the world of growing your own top-quality cannabis right at home with our "Cannabis DIY" online course. This step-by-step program will take you through everything you need to know to grow the best buds, from setting up your grow space to harvesting and drying your plants.
Our teachers will walk you through all of the important skills and tricks to get a huge crop of strong, tasty bud.
You'll find out how to pick the best strains for your setup, grow your plants using natural and organic methods, and give them the perfect food and care to get the most buds possible.
As you go through the course, you'll have access to detailed videos, fun quizzes, and a group of friendly growers who love cannabis as much as you do. You can expect 1:1 hands on support from our experienced mentors, who will be there to help you with any questions or problems you might have along the way.
By the time you finish the "Cannabis DIY" program, you'll have the knowledge and practice to grow amazing cannabis at home, all by yourself. Whether you're totally new to growing or you've tried it before and want to get better, this course will help you become a master cannabis grower and enjoy your own top-quality buds for years to come.
The CK Blog
What your Going
to Love about us.
We go beyond expectations so you can enjoy the grow. Our customers rave about the service, selection, and savings they discover here every day.

Online Course
In this comprehensive Cannabis DIY course, you'll learn everything you need to know to successfully cultivate your own top-quality cannabis plants at home. Our expert will guide you through each step of the process, from selecting the right strains and setting up your grow space to mastering advanced techniques for maximizing yields and potency.

Coaching
Take your cannabis growing skills to the next level with our personalized 1-on-1 coaching sessions. Our expert instructor will work closely with you to assess your unique needs, challenges, and goals, providing tailored guidance and support to help you achieve optimal results in your home grow.
Why you should start Growing ?
Hey, have you ever thought about growing your own cannabis? It might seem tough, but it's totally worth it. You'll have complete control over the quality and save a ton of money.
When you grow your own, you know exactly what's in it – no harmful chemicals. Plus, you get to choose your favorite strains and make it just how you like.
Growing cannabis is also a really rewarding hobby. It's amazing to watch your plants grow from seeds into beautiful, bud-filled plants. And when you harvest, you'll feel so proud of what you made.
The best part? You don't need to be an expert. Our Cannabis DIY course will give you all the knowledge and support you need. We'll guide you through every step, from setup to harvest.
So why not give it a try? You'll have a blast learning something new and end up with amazing cannabis that you grew yourself. There's nothing like it. Start your cannabis growing journey today!
Gallery
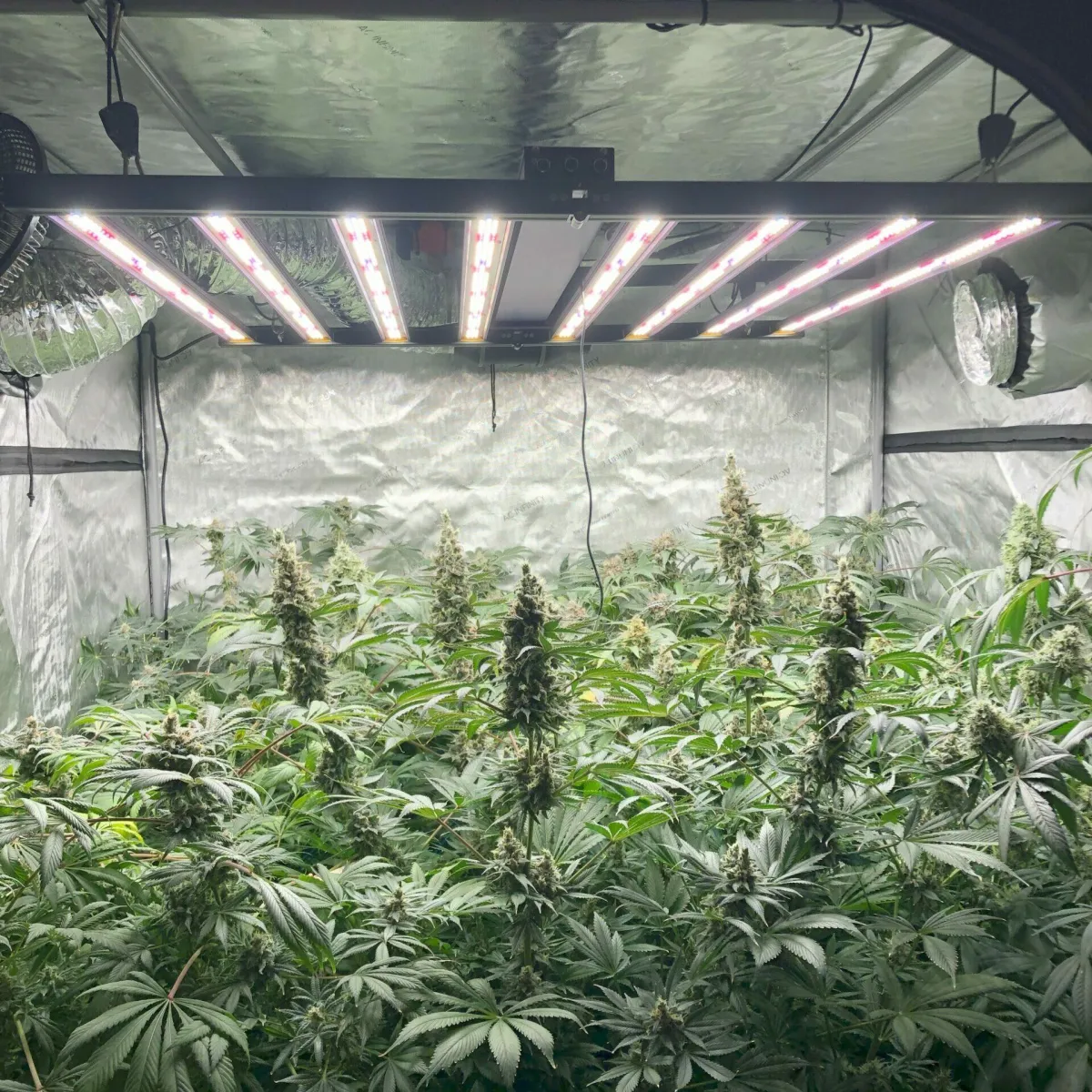
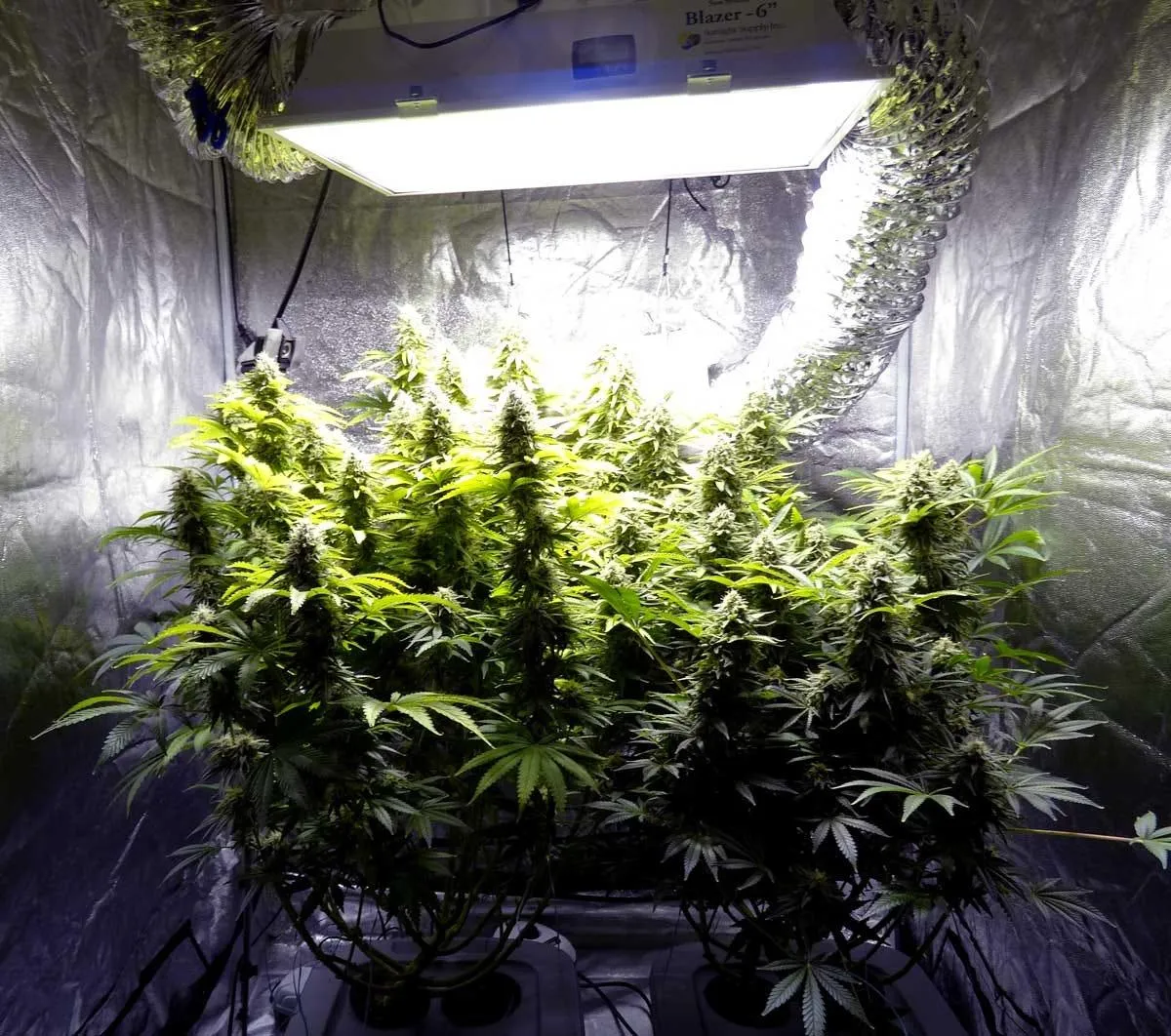
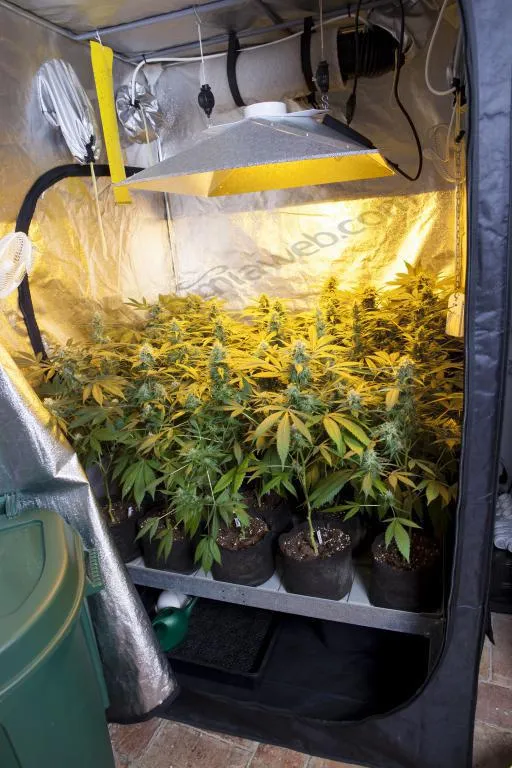
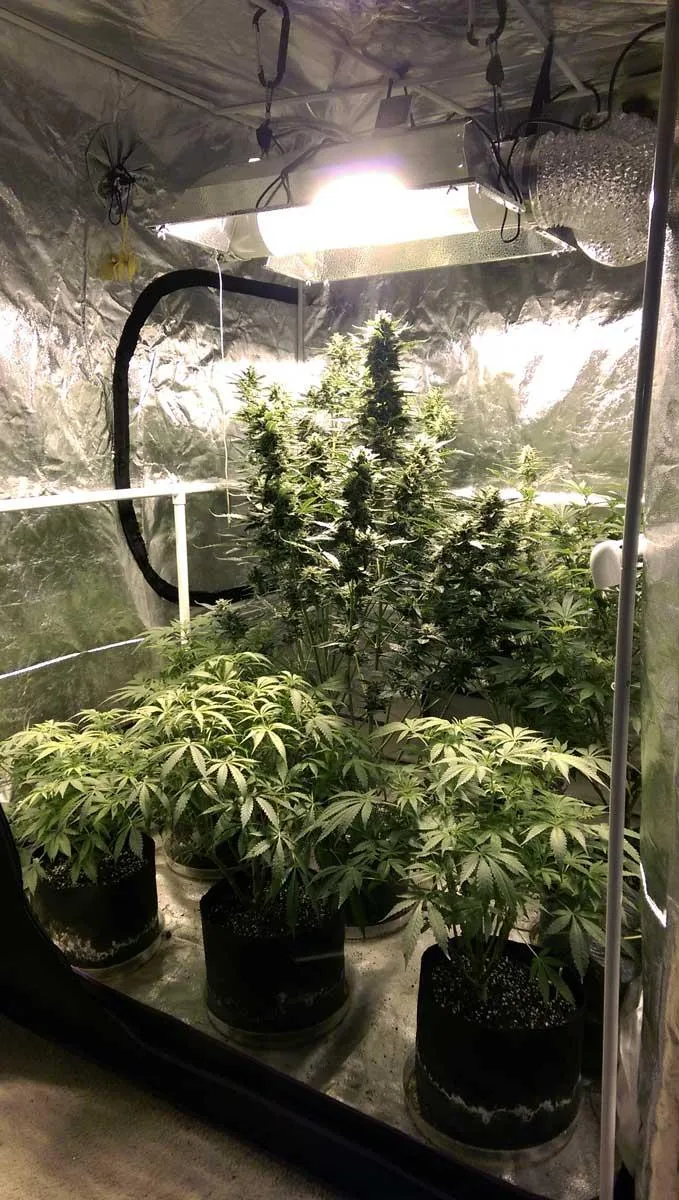




It's Time to Find Your Perfect Strain
Discover the perfect cannabis strains for your home grow with Cannabis Khan's innovative Strain Selection AI Agent! Simply click the button below to access our cutting-edge tool and answer a few quick questions about your grow setup, experience level, and desired effects. Our AI algorithm will analyze thousands of data points to generate personalized strain recommendations tailored to your needs, complete with detailed profiles on yield, flowering time, optimal conditions, and effect/flavor profiles. Take the guesswork out of strain selection and unlock the full potential of your homegrow - click now to find your ideal cannabis match!
Questions? We Have Answers!
Is it legal to grow cannabis at home?
The legality of growing cannabis at home varies depending on your location and the specific laws in your area. Some states and countries have legalized home cultivation for personal use, while others have more restrictive policies. It's crucial to research and understand the laws in your jurisdiction before starting your home grow. Our course provides general information, but it's your responsibility to ensure compliance with local regulations. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Legality_of_cannabis_by_U.S._jurisdiction
How long does it take to grow cannabis from seed to harvest?
The total time from seed to harvest varies depending on the strain, growing conditions, and techniques used. On average, cannabis plants take about 3-5 months to complete their life cycle. This includes the germination phase (1-2 weeks), vegetative phase (3-8 weeks), and flowering phase (6-12 weeks). However, factors such as the specific strain, light cycle, and environmental conditions can influence the growth rate and harvest timeline. Our course provides detailed information on each growth stage and offers tips for optimizing your timeline.
What is your refund policy?
Refund Policy: All sales of our Cannabis DIY course and related digital products are final. Due to the nature of digital products, we are unable to offer returns, refunds, exchanges, or credits for partially used or unused courses, coaching sessions, or other digital products. By completing your purchase, you acknowledge that you have read and agree to this refund policy. If you have any questions or concerns about the course content or your purchase, please contact our customer support team at [email protected] prior to making your purchase.
Get In Touch
Address: 7506 W 10th Avenue, #3, Lakewood Colorado 80214
Email: [email protected]
Phone: (716) 790-9908
Hours of Operation:
Mon - Sat 8am to 6pm
Sunday – Closed










Facebook
Instagram
X
Youtube